Phone
+33 (0)1 76 54 08 64
Address
66 avenue des Champs-Élysées
75008 Paris – France
A cell migration assay is a laboratory technique used to study how cells move in response to stimuli. It's crucial for understanding processes like tissue repair and cancer metastasis.
Common assays include:
These assays help researchers explore factors influencing cell movement and are essential for various biological studies.
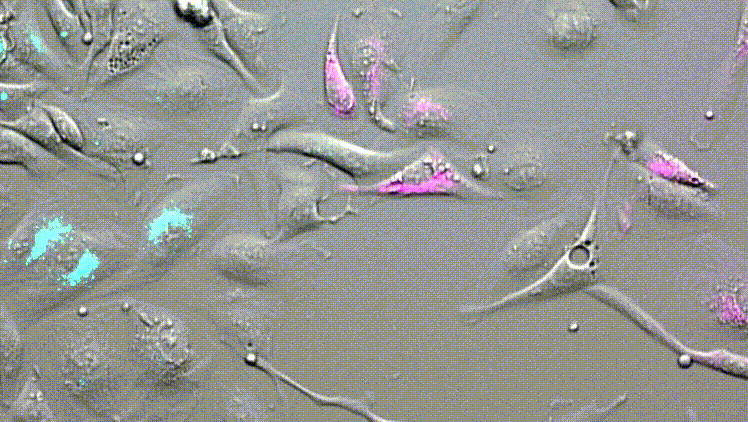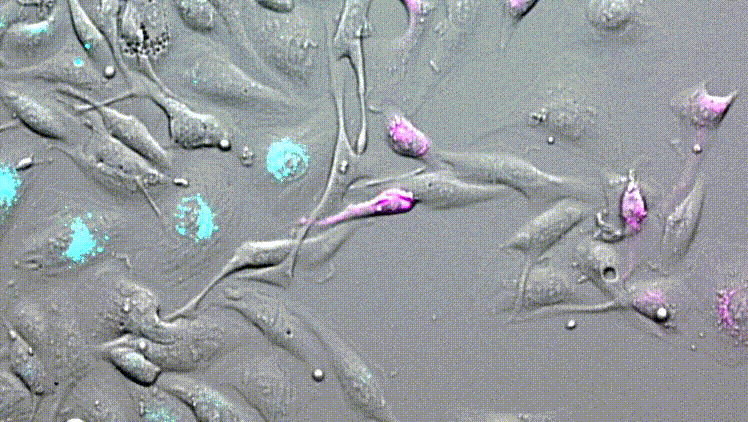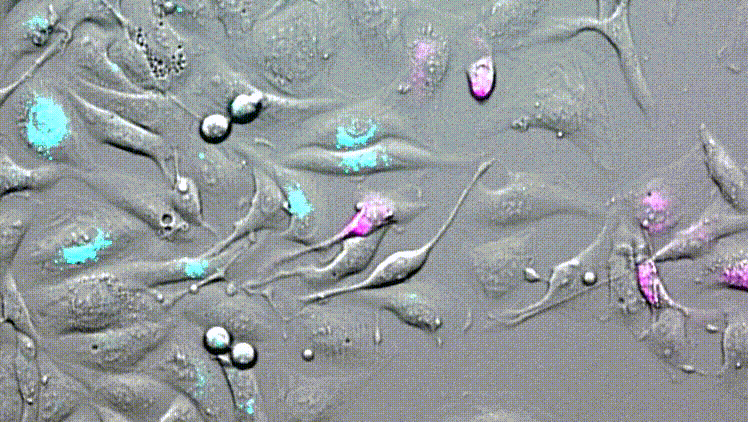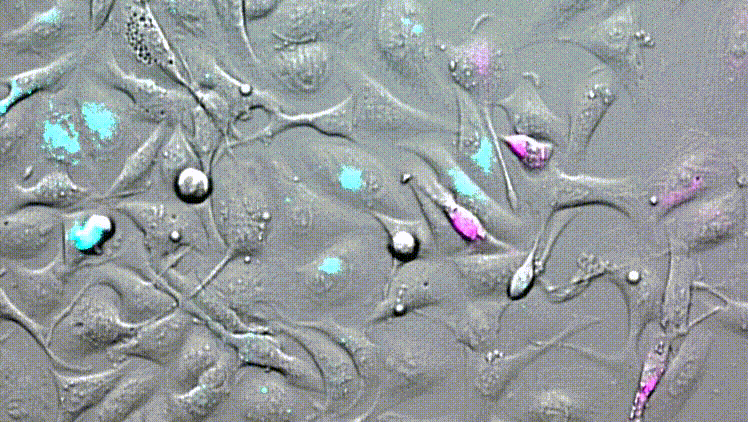
LBL-Dye CellTag 580 and LBL-Dye CellTag 717 are two Cellular Tracers particularly well-adapted for cell migration assays.
After 2 days of acquisition, cells continue to divide and move. We visualize the cellular movements and the mixture of cells that are carried out.
No phototoxicity, no photobleaching, and no dye passive transfer are visible for all acquisition time.
Product citations :
The efficacy of fluorescence-guided surgery in facilitating the real-time delineation of tumours depends on the optical contrast of tumour tissue over healthy tissue. Here we show that CJ215—a commercially available, renally cleared carbocyanine dye sensitive to apoptosis, and with an absorption and emission spectra suitable for near-infrared fluorescence imaging (wavelengths of 650–900 nm) and shortwave infrared (SWIR) fluorescence imaging (900–1,700 nm)—can facilitate fluorescence-guided tumour screening, tumour resection and the assessment of wound healing...
The nuclear receptor, Nurr1, is critical for both the development and maintenance of midbrain dopamine neurons, representing a promising molecular target for Parkinson’s disease (PD)...
Cell-to-cell communication via tunneling nanotubes (TNTs) is a challenging topic with a growing interest. In this work, we proposed several innovative tools that use red/near-infrared dye labeling and employ lifetime-based imaging strategies to investigate the dynamics of TNTs in a living mesothelial H28 cell line that exhibits spontaneously TNT1 and TNT2 subtypes...
Proimaging